All Categories
Featured
Two individuals acquisition joint annuities, which supply a guaranteed revenue stream for the remainder of their lives. If an annuitant passes away throughout the circulation duration, the staying funds in the annuity may be passed on to an assigned beneficiary. The particular alternatives and tax implications will depend upon the annuity agreement terms and applicable laws. When an annuitant dies, the passion earned on the annuity is managed in different ways relying on the kind of annuity. In many cases, with a fixed-period or joint-survivor annuity, the passion remains to be paid to the enduring recipients. A fatality advantage is a function that guarantees a payment to the annuitant's recipient if they pass away before the annuity repayments are worn down. The schedule and terms of the fatality benefit might differ depending on the specific annuity agreement. A sort of annuity that stops all settlements upon the annuitant's fatality is a life-only annuity. Understanding the conditions of the death benefit prior to purchasing a variable annuity. Annuities undergo tax obligations upon the annuitant's death. The tax obligation therapy relies on whether the annuity is held in a certified or non-qualified account. The funds go through revenue tax in a qualified account, such as a 401(k )or individual retirement account. Inheritance of a nonqualified annuity normally causes taxes just on the gains, not the whole quantity.
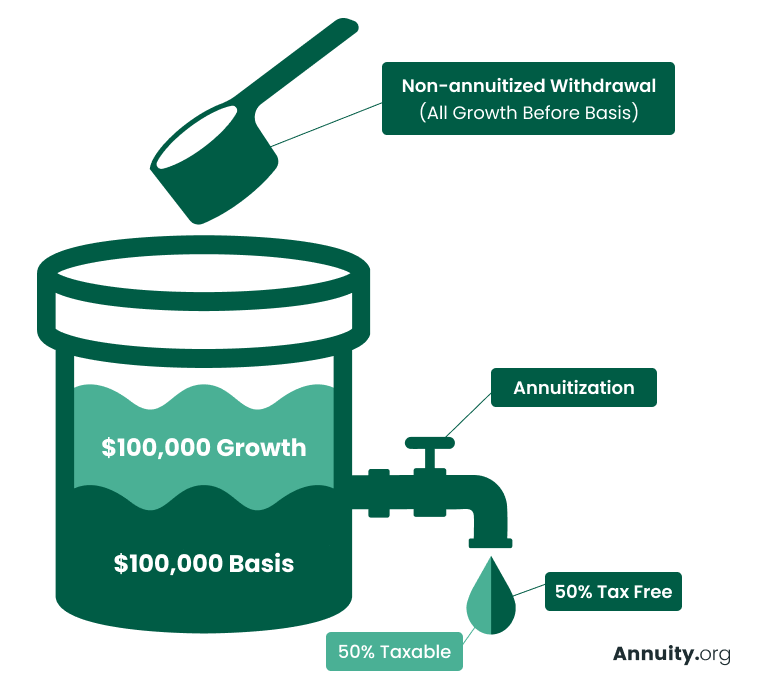
The original principal(the quantity originally transferred by the moms and dads )has currently been tired, so it's not subject to taxes once more upon inheritance. The incomes portion of the annuity the interest or investment gains accrued over time is subject to earnings tax obligation. Typically, non-qualified annuities do.
have passed away, the annuity's advantages normally change to the annuity proprietor's estate. An annuity proprietor is not legally called for to educate present beneficiaries concerning adjustments to recipient classifications. The decision to change beneficiaries is typically at the annuity proprietor's discretion and can be made without alerting the present recipients. Because an estate practically does not exist till an individual has died, this recipient designation would just enter result upon the death of the called person. Normally, once an annuity's proprietor passes away, the designated beneficiary at the time of fatality is entitled to the benefits. The spouse can not alter the recipient after the proprietor's fatality, also if the recipient is a small. Nevertheless, there might specify arrangements for managing the funds for a minor beneficiary. This usually includes designating a lawful guardian or trustee to manage the funds up until the youngster maturates. Generally, no, as the recipients are exempt for your debts. However, it is best to speak with a tax obligation expert for a particular solution pertaining to your situation. You will continue to receive repayments according to the contract schedule, however trying to get a round figure or lending is most likely not a choice. Yes, in mostly all cases, annuities can be inherited. The exception is if an annuity is structured with a life-only payment choice through annuitization. This sort of payment ceases upon the death of the annuitant and does not give any type of residual worth to heirs. Yes, life insurance policy annuities are usually taxed
When withdrawn, the annuity's revenues are exhausted as ordinary income. The major quantity (the preliminary investment)is not exhausted. If a beneficiary is not called for annuity advantages, the annuity proceeds usually most likely to the annuitant's estate. The distribution will comply with the probate process, which can delay repayments and might have tax ramifications. Yes, you can call a depend on as the recipient of an annuity.
Annuity Fees inheritance and taxes explained
This can give better control over just how the annuity advantages are dispersed and can be part of an estate preparation strategy to manage and secure properties. Shawn Plummer, CRPC Retirement Planner and Insurance Coverage Agent Shawn Plummer is a certified Retired life Organizer (CRPC), insurance coverage representative, and annuity broker with over 15 years of firsthand experience in annuities and insurance coverage. Shawn is the owner of The Annuity Professional, an independent on the internet insurance
agency servicing customers across the USA. Via this system, he and his group goal to get rid of the guesswork in retired life preparation by assisting people locate the ideal insurance policy protection at one of the most competitive rates. Scroll to Top. I understand every one of that. What I do not comprehend is just how in the past entering the 1099-R I was revealing a reimbursement. After entering it, I currently owe taxes. It's a$10,070 difference between the reimbursement I was expecting and the taxes I currently owe. That appears really extreme. At most, I would have anticipated the refund to minimize- not entirely disappear. An economic consultant can assist you make a decision just how ideal to manage an acquired annuity. What happens to an annuity after the annuity owner passes away relies on the terms of the annuity agreement. Some annuities merely stop dispersing income settlements when the owner passes away. Oftentimes, however, the annuity has a fatality advantage. The beneficiary might obtain all the staying cash in the annuity or a guaranteed minimum payment, typically whichever is greater. If your moms and dad had an annuity, their contract will specify who the beneficiary is and might

right into a pension. An inherited individual retirement account is a special pension made use of to disperse the properties of a deceased individual to their beneficiaries. The account is signed up in the dead person's name, and as a recipient, you are incapable to make added payments or roll the acquired IRA over to one more account. Just certified annuities can be rolledover right into an inherited IRA.
Latest Posts
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments Everything You Need to Know About Annuity Fixed Vs Variable What Is the Best Retirement Option? Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Retirem
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Choices What Is Choosing Between Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity? Features of Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Pr
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments A Closer Look at How Retirement Planning Works What Is Fixed Income Annuity Vs Variable Growth Annuity? Pros and Cons of Various Financial Option
More
Latest Posts